Pucciniastrum goeppertianum
Alternate hosts: Vaccinium spp.
- Possible yellowing areas on infected needles
- White, tube-like fruiting structures on the underside of infected needles
- Trees near alternate hosts (Vaccinium spp. such as huckleberry, wild blueberry, and cranberry)
- Current season needle necrosis
- Uredinopsis needle rust
- Observe trees in areas near alternate hosts.
- Look for yellowing (often banded) on current season needles.
- Remove and destroy alternate hosts near plantation.
- Spray protective fungicides (if needed) on new developing shoots.
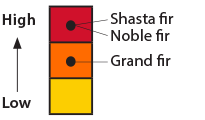
- High susceptibility: Shasta fir, Noble fir
- Medium susceptibility: Grand fir

- Look for white, tube-like structures on the underside of infected needles: All year round
- Check for alternate hosts (Vaccinium spp.): Mid-June through November
- Use fungicides to protect new growth: Mid-May through Mid-June
- Remove and destroy alternate hosts: Mid-August through September


