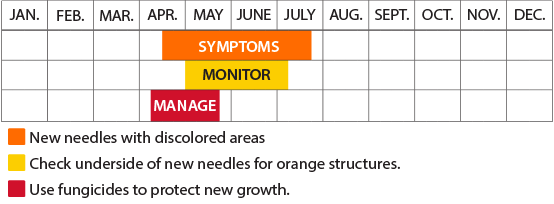
- Slight yellowing on infected newly emerging needles
- Cream to yellow fruiting bodies 2 weeks after initial symptoms
- Discolored areas become necrotic, and the needles shrivel and shed during the following 4 to 6 weeks.
- Severely damaged shoots become cankered and die.
- Diseases
- Insects
- Disorders
- Damage
- Weather Damage
- Frost Damage
- Winter Injury
- Drought
- Heat Damage
- Chemical Damage
- 2, 4-D and Triclopyr
- Fertilizer Burn
- Glyphosate (Roundup)
- Triazines
- Vertebrate Damage
- Deer, Elk, Mice & Voles
- Rabbits & Birds
- Mechanical Damage
- Mechanical Damage
- About
- Order