(Heterobasidion root rot), Heterobasidion annosum
- Declining leader growth
- Dark, irregular-shaped staining in the center of cut trees
- Dead trees near old stumps
- Small white mounds (fungus) on the bark near ground line
- Fields after multiple rotations without stump removal
- Trees planted near stumps
- Other root and canker diseases
- Drought
- Examine stumps of harvested and dead trees.
- Consider stump removal prior to replanting.
- Treat freshly cut stumps of healthy trees with borax (Sporax) to prevent infection by windborne spores.
- Plant resistant species.
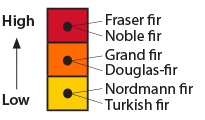
- High susceptibility: Fraser fir, Noble fir
- Medium susceptibility: Grand fir, Douglas-fir
- Low susceptibility: Nordmann fir, Turkish fir

- Look for declining growth, yellowing, dead trees (most likely during moisture stress): Mid-April through Mid-December
- Examine stumps at harvest season: November
- Remove stumps: March through Mid-July
- Treat stumps at harvest: Mid-October through Mid-December


